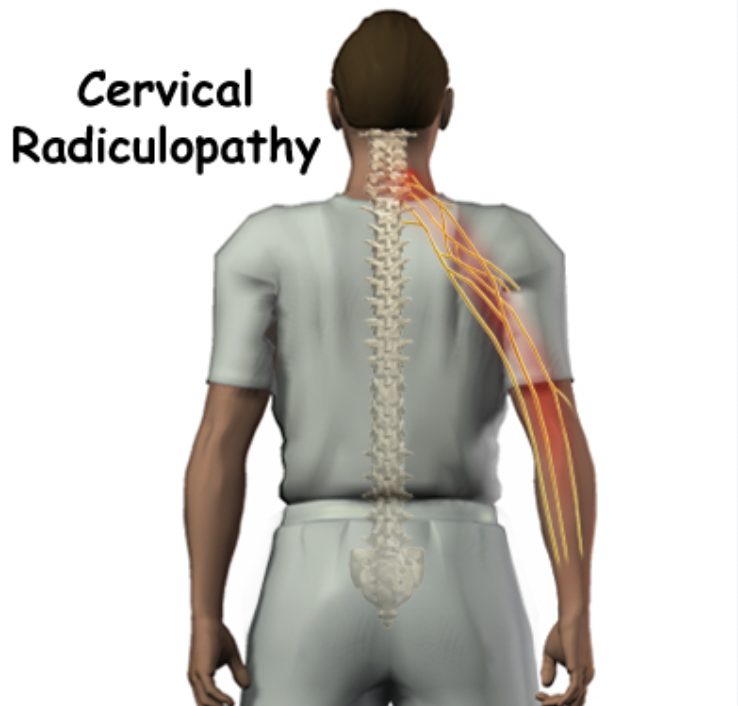
Cervical spine is formed of 7 cervical vertebrae. There are 8 cervical nerve roots. The entry point of cervical intervertebral foramen is the narrowest part and this is the place where compression of the nerve root occurs often. Anterior nerve root compression is caused due to osteophytes and protruding discs whereas posterior nerve root compression is due to articular process,
ligamentum flavum and per radicular fibrous tissue. Nerve roots lack perineurium so the nerves are more vulnerable to mechanical injury. Blood supply are less leading to ischemic changes of nerve roots.
Cervical radiculopathy is also known as Pinched Nerve. This is a condition caused by nerve compression from herniated disc material or osteophytes from arthritic bone spurs. Degenerative spondylitis changes lead to narrowing of intervertebral foramen or literally stenosis. Stenosis cause impingement of the nerve root which leads to both sensory and motor dysfunctions. The major four pathologies behind cervical radiculopathy are compression, irritation, traction and lesion on the root of nerves.
Causes of Cervical radiculopathy
Major causes
Cervical radiculopathy affects people of all ages. When degenerative changes lead to cervical foraminal stenosis it results in the narrowing of openings of the vertebrae causing pinched nerves. It happens most often in people of middle age category.
Disc herniation occur with physical activity by careless bending of the body, lifting, pulling or lifting. It leads to injury or inflammation in the nerve root.
Minor causes
Spinal infections
Benign tumors
Malignant tumors
Symptoms
cervical radiculopathy affects the functional efficiency of nervous system caused due to the damage in the root of nerves and results into obstruction in the chemical messaging between arm and brain centres. Damage to the nerve roots results in pain and loss of sensation along the dermatological distribution. Major symptom is pain that is radiating in nature into the arm, neck, chest upper back and shoulders.
Numbness or tingling sensation in the fingers or arms is the sensory derangement whereas muscle weakness, lack of coordinated movements or reflex errors are the motor damage aspects.
Differential diagnosis
We consider history, physical examination and radiological findings for the differential diagnosis. The conditions which mimic cervical radiculopathy are
Cervical myelopathy
Ligamentous instability
Peripheral nerve disorders
Brachial plexus pathology
Spinal tumors
Investigations and interpretation
Intervertebral foraminal narrowing can be read from X ray of cervical region. CT Scan and MRI Scan give more detailed presentation of disc injury or herniation.
Ayurvedic management of cervical radiculopathy
Ayurveda aims at stabilising the vitiated doshas and bringing the normal balance of tridoshas. Cervical radiculopathy is correlated with visvachi in Ayurveda which is a Vata predominant disease state where the vata causes cervical pain and radiating pain towards the affected arm. In Samwarthika, physicians keenly observe the doshic imbalance and causes behind and advises the required herbal combinations internally and also select the apt panchakarma therapies and tailors the combinations into the pathological states and stages. Along with treatment strategies, special Yoga trainings also provide with the supervision of experienced medical professionals. Total body functions are analysed and special diet advised as per the requirement of the proper health of the patient. This results into the faster relief from the pathological states. Recovery, relief, detoxification and rejuvenation are the base of the treatments which is provided with customized person specific style. Dhanyamladhara, choornapindasveda, pathrapotalasveda, greevavasthi, pizhichil etc. are provided according to the condition of the patients and severity of the disease. Comprehensive treatment in Samwarthika scientifically cure the condition and revitalize the patients carefully. Samwarthika stands for the wellness of the patient and develop unique treatment approach to each patient.
Thank you.