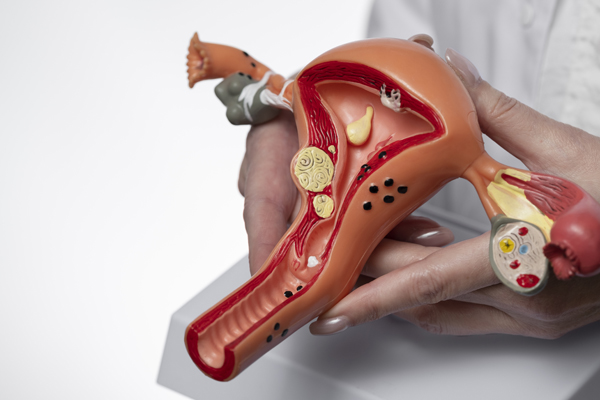
What is PCOS?
PCOS or Poly Cystic Ovarian Syndrome is a complex set of hormonal disorders affecting women in the fertile reproductive age. Typical signs and symptoms include hormonal imbalances, weight gain, skin problems, excessive male pattern hair growth, and irregular and usually delayed menstrual cycles. The cardinal sign is the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries. An excess of androgen or male hormone levels are found. PCOS ovaries show multiple follicles or cysts which are small collections of fluid, and these ovaries fail to regularly release eggs.
What are the causes of PCOS?
Causes are not established however PCOS is considered as a lifestyle disorder. An unhealthy sedentary lifestyle combined with indiscriminate unhealthy eating habits are the major triggers for PCOS. Other factors attributed are genetics, insulin resistance, and hormonal imbalances
What are the classical Symptoms of PCOS?
PCOS’s common symptoms are
- Irregular, infrequent, or absent menstrual periods with scanty or heavy flow
- Excessive male pattern hair growth or hirsutism
- Acne and eruptions
- Acanthosis nigricans or skin discoloration on the shoulder, back of the neck, axilla, etc.
- Weight gain, overweight or obesity. Lean PCOS is also seen
- Fertility problems
- Mood swings, fatigue, and sleep disturbance
Complications of PCOS include primary and secondary infertility, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular diseases
What are the types of PCOS?
4 types of PCOS are Insulin-resistant PCOS, Inflammatory PCOS, Hidden-cause PCOS, and Pill-induced PCOS.
- Insulin-resistant PCOS: Most common and caused by unhealthy lifestyle and environment like smoking, sugar, pollution, and trans-fat. The presence of high levels of insulin prevents ovulation and triggers testosterone over production
- Pill-induced PCOS: Caused by the use of birth control pills and is curable once the use is stopped. However long-term use can make the condition worse
- Inflammatory PCOS: Inflammation due to factors like due to stress, toxins of the environment, and inflammatory dietary materials like gluten prevents ovulation leading to hormonal imbalance and production of androgens
- Hidden PCOS: An easier to manage PCOS, is caused by conditions like thyroid disease, deficiency of iodine, vegetarian diet induced zinc deficiency, and use of artificial sweeteners.
What are the tests for PCOS?
Ultrasound scans and blood tests are done to diagnose PCOS. Blood tests include Fasting Blood Sugar, Glucose Tolerance Test, Hormone assays like thyroid function test, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), progesterone, testosterone, and prolactin
Is there a cure for PCOS in Ayurveda?
PCOS is termed Artava Kshaya or decreased menstruation and is said to be a condition of Tridosha imbalance, particularly Vata and Kapha. Hence the management of PCOS in Ayurveda is the restoration of Tridosha balance, Agni correction or correcting metabolism, improving digestion, and promoting a healthy lifestyle. The treatment is a combination of Ayurveda medicines, Panchakarma therapies, Yoga, Diet, and Lifestyle modification
What are the dos and Don’ts in PCOS?
Do’s
- Balanced and nutritious timely diet
- Sufficient water intake
- Healthy weight
- Yoga and Meditation
- Yoga postures of Suryanamaskara and Chakkichalana
- Pranayama like Kapalabhati and Ujjayi
- Active positive lifestyle
- Positive stress management and timely sleeping habits
- Eat local, fresh, organic foods diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Exercises like brisk walking, swimming, Zumba, and aerobic exercises
Don’ts
- Processed and sugary food. Reduce saturated fats, salt, and refined sugar.
- Unhealthy habits such as smoking, alcohol, psychotropics and narcotics
- Skipping Meals
- Skipping Doctor’s Appointment
- Neglecting mood swings and mental health
- Negative stress
What are the scientific studies on PCOs and Ayurveda?
Poly Cystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrinopathy in women of reproductive age, resulting from insulin resistance and compensatory hyperinsulinemia. This results in adverse effects on multiple organ systems and may result in alteration in serum lipids, anovulation, abnormal uterine bleeding, and infertility. According to the Ayurvedic view, PCOS can be correlated with Aarthava Kshaya. It was revealed that most of the subfertility patients who were presented at Osuki Ayurveda Centre suffered from PCOS. Therefore the present study was carried out for the clinical evaluation of the efficacy of Ayurveda treatment regimen on subfertility with PCOS. A total of 40 patients were selected by using the purposive sampling method. According to the Ayurveda theories of Shodhana, Shamana, and Tarpana, the treatment was conducted in 3 stages for the duration of 6 months. The response to the treatment was recorded and therapeutic effects were evaluated by symptomatic relief and through Trans Vaginal Scan and LH, FSH hormone levels. The results revealed that subfertility due to PCOS can be cured successfully by using this Ayurveda treatment regimen. Dayani Siriwardene SA, Karunathilaka LP, Kodituwakku ND, Karunarathne YA. Clinical efficacy of Ayurveda treatment regimen on Subfertility with Poly Cystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS).
Ayu. 2010 Jan;31(1):24-7. doi: 10.4103/0974-8520.68203. PMID: 22131680; PMCID: PMC3215317.