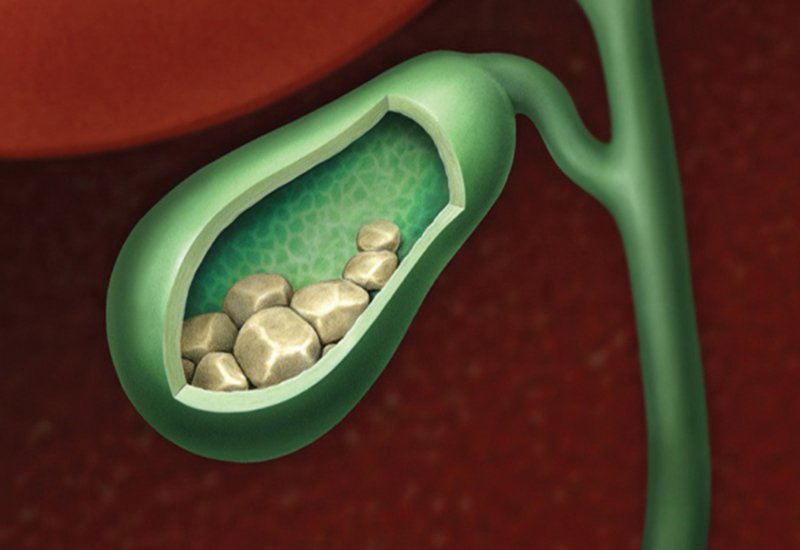
Symptoms of Gallbladder Stones
Gallstones can often exist without any noticeable symptoms. However, when a gallstone becomes stuck in a duct, causing an obstruction, it can lead to the emergence of one or more of the subsequent symptoms:
- Intense Upper Right Abdominal Pain: Sudden and swiftly intensifying pain in the upper right section of the abdomen.
- Rapid Central Abdominal Pain: Abrupt and escalating pain occurring in the middle of the abdomen, situated just beneath the sternum.
- Discomfort between Shoulder Blades: Uncomfortable sensations experienced between the shoulder blades.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Sensations of nausea or an inclination to vomit.
- Discomfort triggered by gallstones can persist for varying durations, ranging from a few minutes to several hours.
Causes of Gallbladder Stones
The exact causes of gallstone formation are not definitively understood. Medical professionals hypothesize that gallstones may develop under the following circumstances:
- Elevated Cholesterol in Bile: Ordinarily, the chemicals present in your bile are sufficient to dissolve the cholesterol produced by your liver. However, when your liver excretes more cholesterol than can be dissolved by the bile, the surplus cholesterol could crystallize, eventually leading to the formation of stones.
- Excessive Bilirubin in Bile: Bilirubin, a byproduct resulting from the breakdown of red blood cells, is produced in your body. Certain conditions, such as liver cirrhosis, biliary tract infections, and specific blood disorders, can cause an overproduction of bilirubin by the liver. This surplus bilirubin might contribute to the creation of gallstones.
- Improper Gallbladder Emptying: When the gallbladder fails to empty completely or frequently enough, bile can become highly concentrated. This concentrated bile may be a contributing factor in the development of gallstones.