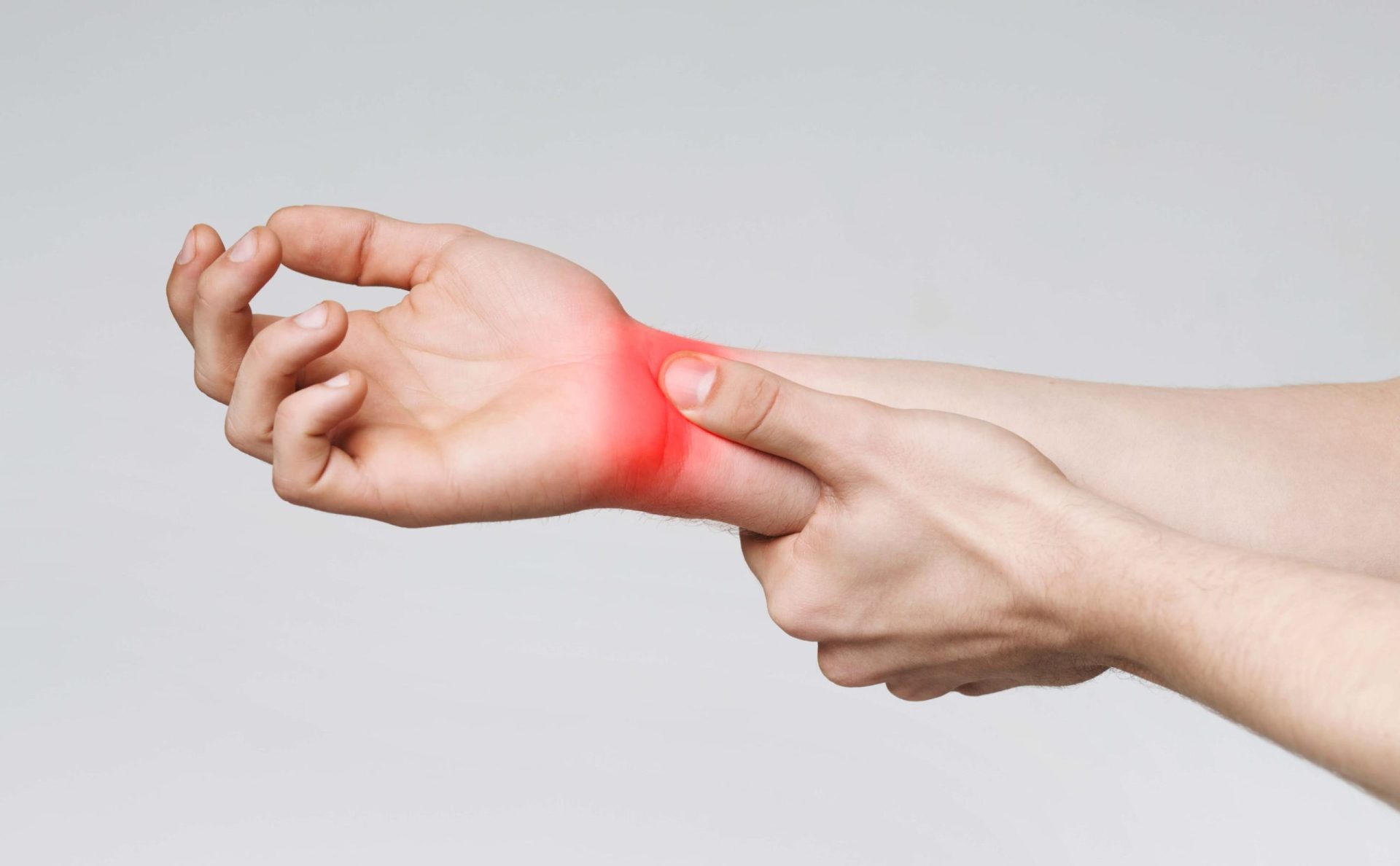
Have you ever seen anybody complaining of pain, numbness, weakness in the hand or often squeezing their hand frequently after doing some work like lifting books,luggage or typing on their computer?
Peripheral neuropathies are common medical conditions seen in our daily OPD. They present with symptoms like numbness, tingling sensation, aching type of pain. When it comes to upper extremities, these symptoms are shown in a most common condition called Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), which is common in middle-aged females.
What is carpel tunnel syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel is a passage way from the wrist to the hand, made of tendons, ligaments, and bones. The important structure passing through the carpal tunnel is the Median nerve. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Is a type of Entrapment Neuropathy, where direct pressure over a single nerve is causing the symptoms. In the case of CTS direct pressure is acted upon the Median nerve, which supplies the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and lateral part of the ring finger. The cause for pressure may be due to swelling or degeneration of one of the tendons passing through the tunnel. This compression of median nerve leads to symptoms like pain, tingling sensation and numbness of the hand and the fingers. The symptoms are experienced in the part of the hand that is supplied by the median nerve.
EXTENSION OF PAIN: The pain extends upward to the arm .The discomfort also extends to the shoulder and forearm.
RISK FACTORS
· Anatomic factors: Include deformity of wrist joint due to fracture/dislocation/arthritis, which will cause a reduction in the size of carpal tunnel and cause compression to Median nerve.
Genetically some patients may have smaller carpal tunnel
· Sex: CTS is seen commonly in females. Females tend to have smaller Carpal tunnel compared to males, which makes the condition more common in females.
· Nerve damaging conditions like chronic illness, Diabetic neuropathy, etc.
· Obesity
· Body fluid retention: As in times of pregnancy and menopause. During Pregnancy, there is increased retention of fluid in the body, which will cause compression to the nerve. Usually, the condition will be resolved after the pregnancy period
· Thyroid disorders
· Kidney failure
· Occupational factors: CTS is seen commonly in people who continuously work with vibrating tools, computers, musical instruments, or on an assembly line that requires prolonged or repetitive flexing of the wrist.
· Idiopathic: Most of the conditions are idiopathic, where the root cause is not known
SYMPTOMS
HOW SHOULD I KNOW THAT I HAVE CTS FOR SURE?
· Tingling or numbness: Felt over hand except for little finger, It is likely to be more during night hours and while holding objects like phone, newspaper, etc. The patient wakes up at night with an aching type of pain, numbness, and tingling sensation. The sensation may travel upwards up to the arm. Usually, people used to shake their hands to get relief from these symptoms.
· Weakness: Over a period of time, the patient may develop weakness of the hand and drop objects.
· One can confirm their condition by a test called “Phalen’s Maneuver” (Wrist flexion test): Press the backs of your hands and fingers together with wrists flexed and fingers pointed downwards. Hold in the same position for 1 minute. If there is a tingle or gets numb, it’s positive for CTS.
· Nerve conduction studies.
HOW DO I MANAGE SYMPTOMS IN EARLIER CONDITION?
When the symptoms are few you can manage them at home. Don’t try when the symptoms got worse)
· Stop any activity that causes numbness and pain
· Provide good rest for your wrists in between activities
· Soothe your wrists with icepacks for 10-15 minutes once in evey 2-3 hours
AYURVEDIC MANAGEMENT & PREVENTION
In Ayurveda the advanced stages of Carpel Tunnel Syndrome can be seen in viswachi (Functional loss of hand ) and Khalli (Viswachi assosciated with low back pain). Both are considered as dysfunction of vata in kandara (abnormal activity of vata in ligaments).Hence it should be under stood as vyana vayu dysfunction within the median nerve.
Management depends upon the stages of disease .
Numbness and reduced sensation phase will be treated with swedana fomentation) and kaphavata samana (maintaining equilibrium by correcting metabolism),
Pain predominant phase will be treated with vatapitta samana (correcting metabolism) and snehana ( improving the stricture by nourishment ),
Wasting / functional loss phase should be treated with vata smana (correcting metabolism) and brmhana (nourishing th structure) .
CTS can be effectively managed through Ayurvedic Panchakarma treatments including rakthamoksha followed by physiotherapy of the wrist joint.
Healthy and lifestyle management
· Take care of your basic health,eat good food and live good life.
· Maintain body weight to normal proportions(corresponding to your BMI)
· Don,t smoke or take alcohol.
Wrist care
· Try keeping your wrist in neutral position
· Use whole hand to hold and lift the objects rather than using only fingers
· When you are using the computer try keeping your wrists straight with the rest your upper limb placed a little higher than the position of your wrists
· When you are doing repeated movements try to switch the movements or activities between both hands.
· Use of ergonomic equipments like wrist rest, mouse pad, etc